About this course
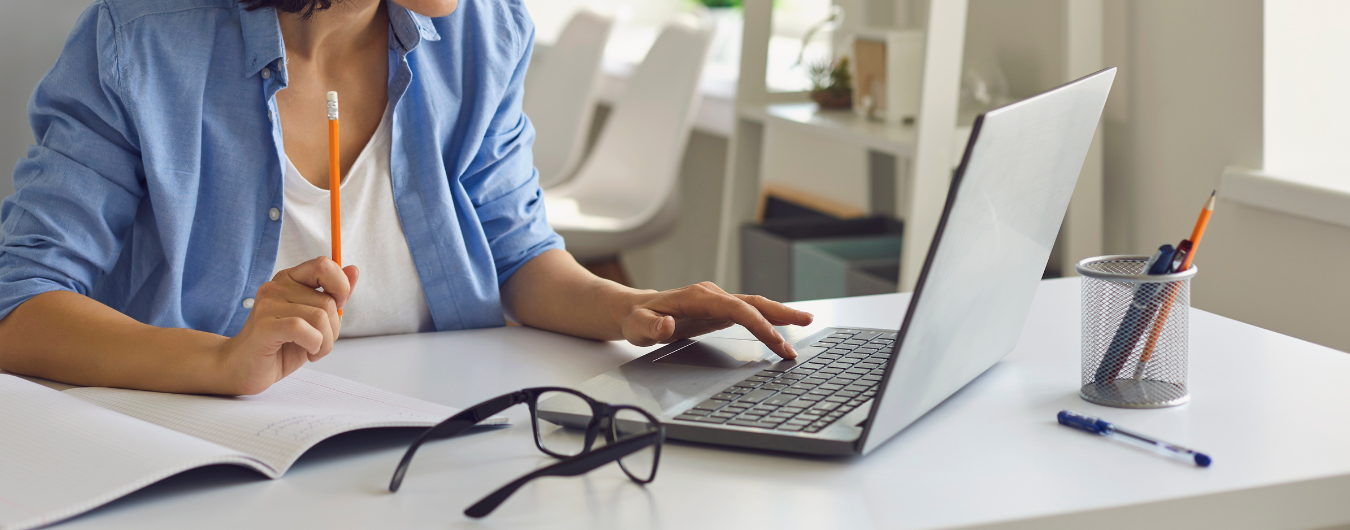
Join our C Programming Live Class, where you can start learning from scratch at any time with personalized 1:1 live sessions. Whether you're a beginner or looking to strengthen your C skills, our flexible and interactive approach ensures effective learning at your own pace. Our classes are designed to provide a hands-on learning experience with real-time coding demonstrations and problem-solving.
🔹 Key Features:
✅ Start Anytime – No fixed batches, join when you're ready!
✅ Live Sessions – Personalized learning with expert guidance.
✅ Beginner-Friendly – Learn from the basics, no prior experience needed.
✅ Hands-on Coding – Live coding, practice exercises & real-world projects.
✅ Doubt Clearing – Get instant solutions to your queries.
🔹 What You’ll Learn:
✅ Fundamentals of C (Variables, Data Types, Operators)
✅ Control Flow (Loops, Conditionals)
✅ Functions and Recursion
✅ Arrays, Pointers, and Strings
✅ Structures and File Handling
✅ Dynamic Memory Allocation
✅ Problem-Solving Techniques
📌 Live Class Features:
🔹 Interactive Teaching – Learn through live coding and explanations.
🔹 Practice Exercises – Get hands-on coding problems after each session.
🔹 Doubt Solving – Ask questions and get instant solutions.
🔹 Project-Based Learning – Work on real-world applications.
🚀 Who Can Join?
✅ Beginners who want to learn C from scratch.
✅ Students preparing for coding interviews.
✅ Anyone looking to strengthen problem-solving skills.
Join us and start your journey to mastering C programming! 💻🔥
Comments (0)
Learn about C programming, its history, and setting up a development environment (IDE & Compiler).
In this session, you will learn the fundamental building blocks of C programming, including syntax rules, variables, and data types. These concepts form the foundation for writing efficient and error-free C programs.
Input and output (I/O) operations in C allow programs to interact with users and external devices by reading and displaying data.
Operators in C are special symbols that perform operations on variables and values. Expressions are combinations of variables, constants, and operators that produce a value. Understanding operators and expressions is crucial for performing calculations, making decisions, and controlling program flow.
C provides various types of operators, including arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, and conditional operators, which are used to build expressions that drive computations and decision-making in a program.
These exercises will help you improve problem-solving skills, build confidence in writing C programs, and strengthen your grasp of operators, expressions, and input/output operations.
Conditional statements in C allow decision-making within a program by executing different blocks of code based on conditions. The primary conditional statements include if, if-else, nested if, else-if ladder, and switch-case. These structures help control the flow of execution by evaluating conditions and executing the appropriate code block.
Loops in C are used to execute a block of code repeatedly until a specified condition is met. They help reduce redundancy, making programs more efficient and easier to manage. The three main types of loops in C are for, while, and do-while, each suited for different scenarios of iteration.
Loop control statements in C allow you to alter the normal flow of loops by skipping iterations, exiting loops , or jumping to a specific part of the program. The three main control statements are break, continue, and goto, each serving a distinct purpose in managing loop execution.
Functions in C allow code modularization by breaking large programs into smaller, reusable blocks. A function is a self-contained piece of code that performs a specific task. C provides library functions (predefined) and user-defined functions (created by the programmer). Understanding functions improves code readability, reusability, and maintainability.
Recursion is a programming technique where a function calls itself to solve smaller instances of a problem. It is widely used in problems that can be broken down into smaller, similar subproblems, such as factorial calculation, Fibonacci sequence, and tree traversals. Understanding recursion helps in writing elegant and efficient solutions for complex problems.
This section is designed to reinforce your understanding of loops, conditional statements, and functions through hands-on problem-solving. These exercises will help improve your logical thinking, coding efficiency, and confidence in implementing key C programming concepts.
An array is a collection of elements of the same data type stored in contiguous memory locations. Arrays allow efficient storage and manipulation of multiple values, making them essential for handling large datasets. C supports one-dimensional (1D), two-dimensional (2D), and multi-dimensional arrays for different applications.
Practice Array
A string in C is a sequence of characters terminated by a null character (\0). Unlike other programming languages, C does not have a built-in string data type; instead, strings are handled as character arrays. String handling is essential for text processing, input validation, and various real-world applications.
Practice String topic
structure in C is a user-defined data type that groups related variables of different data types under a single name. Structures help in organizing and managing complex data efficiently, making them essential for real-world applications like databases, file handling, and system programming.
A union in C is a user-defined data type similar to a structure, but with a key difference: in a union, all members share the same memory location, meaning only one member can store a value at a time. Unions are useful for memory-efficient programming, particularly in low-level system programming and embedded systems.
Practice what you learn in structure and union
A pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable. Pointers are one of the most powerful features in C, allowing efficient memory management, dynamic memory allocation, and direct manipulation of data stored in memory. Mastering pointers is essential for working with arrays, functions, and data structures like linked lists.
Dynamic Memory Allocation (DMA) in C allows the allocation of memory at runtime using special functions from the stdlib.h library. This is useful when the required memory size is not known at compile time. Unlike static memory allocation, where memory is assigned at declaration, DMA enables flexible and efficient memory management.
Practice what you learn in pointer and DMA
File handling in C allows us to store and retrieve data from files, making programs more useful and persistent. Using file operations, we can read, write, modify, and delete data stored in files instead of relying solely on console input/output.
Practice Exercises of file handling
Command-line arguments allow users to pass inputs directly when executing a program from the terminal or command prompt. This enables dynamic and flexible input handling, making programs more versatile. Command-line arguments are passed to the main() function as parameters.
Debugging and error handling are essential for writing reliable and bug-free programs. Debugging helps identify and fix logical and runtime errors, while error handling ensures that programs handle unexpected situations gracefully. In this session, you'll learn various techniques to debug and handle errors efficiently in C.
In this project, you will build a Student Management System using C.
This project will help you apply arrays, functions, file operations, pointers, and error handling in a real-world scenario.
In this project, you will build a Library Management System using C. The system will allow users to add, view, search, update, and delete book records while storing data using file handling. This project will help you apply structures, file handling, functions, loops, and error handling in a practical scenario.